
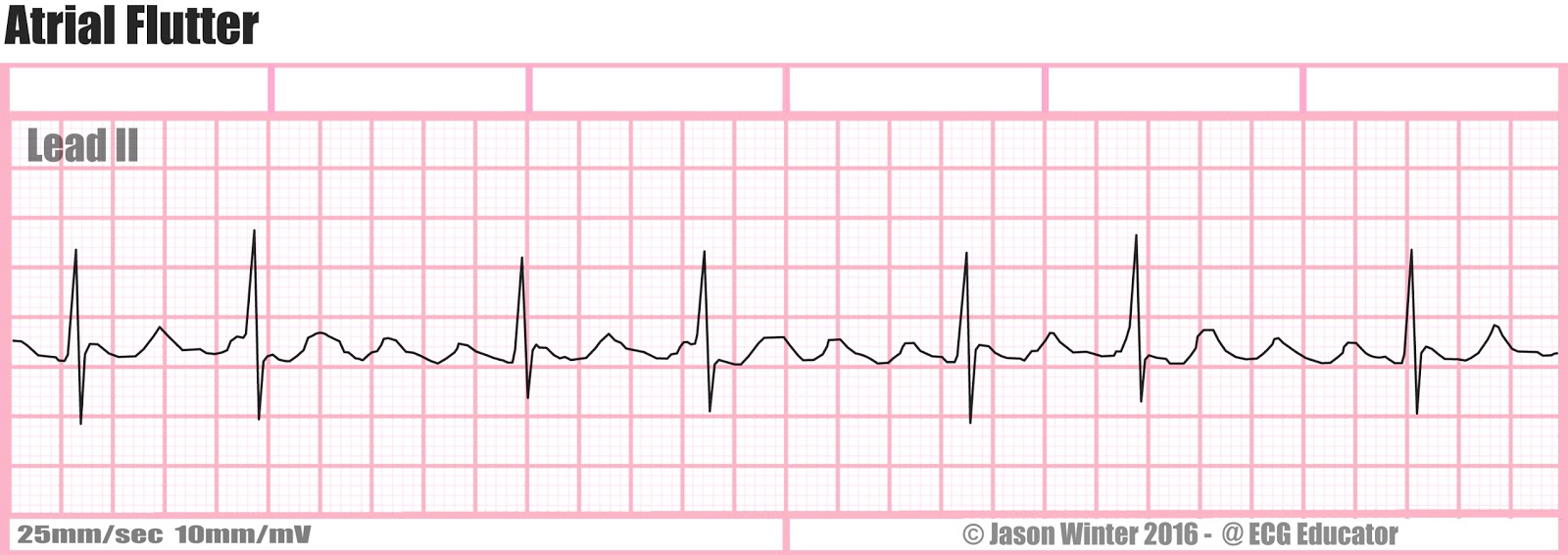
Typical atrial flutter and ecg trial#
RACE-II trial demonstrated that lenient control (goal HR Make sure you are not slowing down a normal physiologic response (e.g.Cardioversion is preferred and treats 96-97% of atrial flutter.Less reactive to PO medication than atrial fibrillation.If mild or no symptoms and pulse only mildly elevated (Amiodarone 150mg over 10min (preferably through central venous access) OR diltiazem 2.5mg/min until HRIndications: ischemic chest pain, SBP 60.Does not meet criteria for typical atrial flutter.Positive flutter waves in inferior leads.Inverted flutter waves in inferior leads.Re-entry circuit of right atrium (IVC and tricuspid valve).Amal Mattu recommends flipping ECG 180 to easily see inverted P waves or speed machine up to 50 mm/s to stretch out ECG.A-fib is completely irregular with no relationship between intervals.Look for: R-R interval that is multiple of P-P interval and mathematical relationship between R-R intervals.Difficult to distinguish from atrial fibrillation.Suggests AV nodal blocking agents or AV node disease.Suspect atrial flutter whenever ventricular rate is 150.Suggests pre-excitation, sympathetic excess, parasympathetic withdrawal, Class 1C anti-arrhythmic use.Hallmark is discordance in flutter wave direction between inferior leads and V1.Flutter waves (sawtooth pattern) in inferior leads.Usually regular unless variable AV conduction present.Cardiac Echo - if signs of new/worsening heart failure.Second Degree AV Block Type I (Wenckeback).Atrial fibrillation/ atrial flutter with variable AV conduction AND accessory pathway (e.g.Atrial fibrillation/ atrial flutter with variable AV conduction AND bundle branch block^.Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (consider if less than or ~120 bpm).Sinus tachycardia with bundle branch block^.Atrial flutter with bundle branch block^.Atrial flutter with variable conductionĪssume any wide-complex tachycardia is ventricular tachycardia until proven otherwise (it is safer to incorrectly assume a ventricular dysrhythmia than supraventricular tachycardia with abberancy).Sinus tachycardia with frequent PACs, PJCs, PVCs.Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT).Idiopathic fascicular left ventricular tachycardia.Atrial tachycardia (uni-focal or multi-focal).Defined by atrial rate of 250-350, classically 300Ĭan be difficult to distinguish from atrial fibrillation Narrow-complex tachycardia.

5.4.1 Anticoagulation Prior to Cardioversion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
